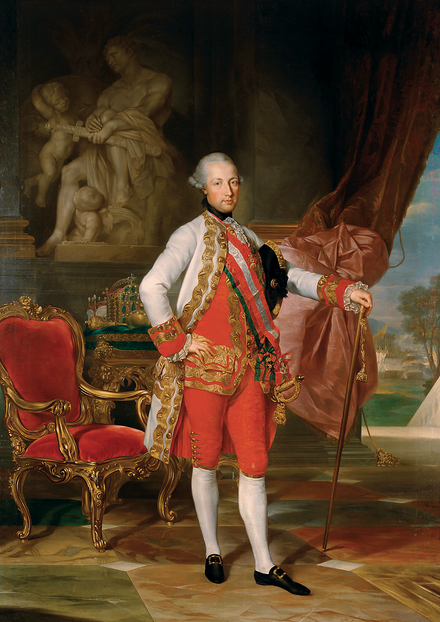
Habsburg Emperor Joseph II tried to reform Austria into “ideal Enlightened state”. He abolished serfdom, removed restrictions against Jews, gave religious freedom to Protestants and Orthodox and tried to weaken power of Catholic church. But as soon he died all his reforms were abolished
Josephinism “Josephists” redirects here. For the medieval heretics, see Josephines. For other uses, see Josephites. Joseph II by Anton von Maron, 1775 Josephinism was the collective domestic policies of Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor (1765–1790). During the ten years in which Joseph was the sole ruler of the Habsburg Monarchy (1780–1790), he attempted to legislate […]